Ingest real time streaming data for time series analysis

This post describes how to ingest sample real time streaming data from PubNub to a Postgres database with the TimescaleDB extension installed and enabled for time series analysis. I wrote a small Node.js app to test and demonstrate how TimescaleDB performs well in fetching results while data is also being ingested in the database. Will be using the following data feed, Market Orders – an artificial data stream that provides the latest market orders for a fictitious marketplace and you can clone or download the GitHub repository from -> https://github.com/sfrechette/stream-sequelize-node.
The Market Orders data feed generates on average 4 inserts per second, if you would to ingest more inserts per second I recommend you look at the following data feed Sensor Network which generates on average 10 inserts per second.
Ingest real time streaming data for time series analysis
Prerequesites
Running this application assumes that you already have an instance of Postgres running and have installed the TimescaleDB extension. If not please refer to the following documentation -> Getting started, installing and setting up -> https://docs.timescale.com/v0.9/getting-started.
Once Postgres with the TimescaleDB extension is installed you will need to execute the following SQL code snippets in your Postgres environment using your preferred tool to connect (I am using pgcli) in order to create the database, create the timescaledb extension, create the schema, and hypertable.
Issue the following SQL statements in your Postgres environment:
create database market_orders;
\c market_orders
create extension if not exists timescaledb cascade;
create table orders (
order_time bigint not null,
trade_type text not null,
symbol text not null,
order_quantity double precision not null,
bid_price double precision not null
);
create index on orders(order_time desc);
create index on orders(trade_type, order_time desc);
create index on orders(symbol, order_time desc);
create index on orders(order_time desc, order_quantity);
create index on orders(order_time desc, bid_price);
-- 86400000000 is in usecs and is equal to 1 day
select create_hypertable('orders', 'order_time', chunk_time_interval => 86400000000);
Installation
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/sfrechette/stream-sequelize-node.git
cd stream-sequilize-node
Next install the dependencies with the following command:
npm install
You will then need to create an .env file in the root folder of the app “stream-sequilize-node” and add configuration values. Copy and paste the following snippet in your .env file and provide the appropriate connectivity information to your Postgres environment:
DB_SERVER_USER_NAME = ""
DB_SERVER_USER_PASSWORD = ""
DB_SERVER_HOST = ""
DB_SERVER_PORT = ""
Usage
You are now ready to start ingesting data, simply issue the following command:
node ingest.js
Sample queries
Assuming that you have been ingesting data for a while (you can modify the time interval in the script below), run some queries to test and validate how Timescale performs nicely in fetching results while data is also being ingested in the database. More data the better 😉
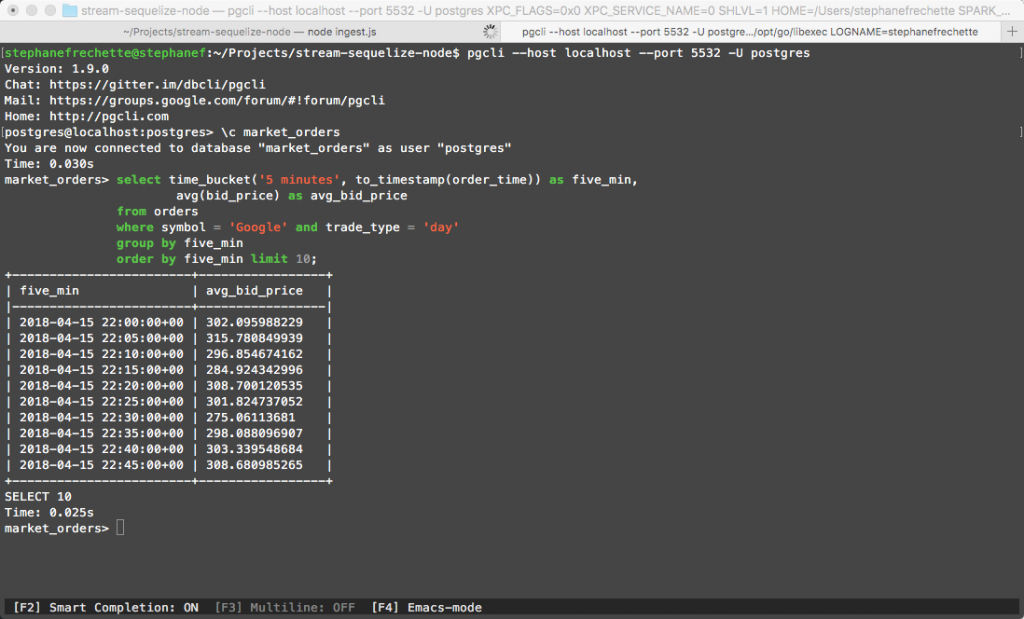
-- Average bid price by 5 minute intervals for Google and day trade type
select time_bucket('5 minutes', to_timestamp(order_time)) as five_min,
avg(bid_price) as avg_bid_price
from orders
where symbol = 'Google' and trade_type = 'day'
group by five_min
order by five_min limit 10;
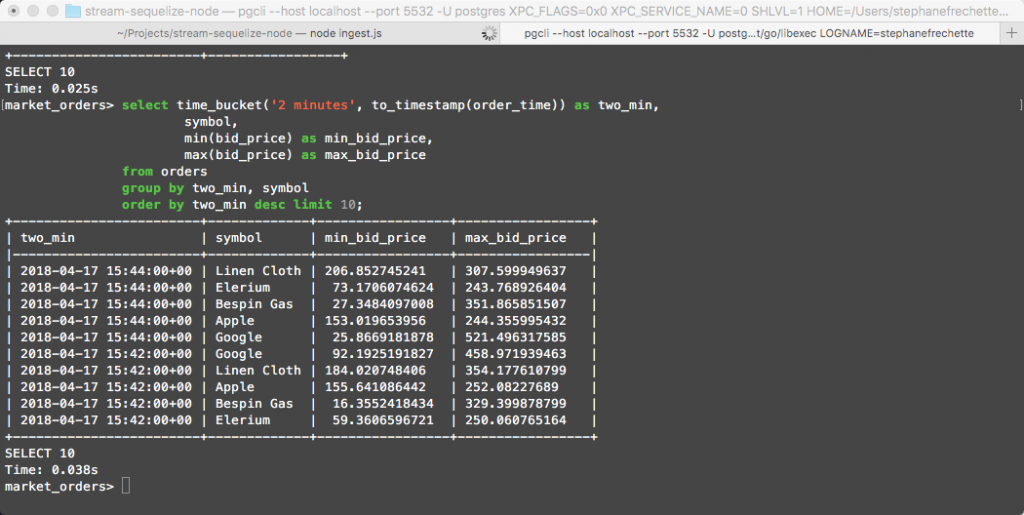
-- Min and Max bid price by 2 minute intervals for all symbols
select time_bucket('2 minutes', to_timestamp(order_time)) as two_min,
symbol,
min(bid_price) as min_bid_price,
max(bid_price) as max_bid_price
from orders
group by two_min, symbol
order by two_min desc limit 10;
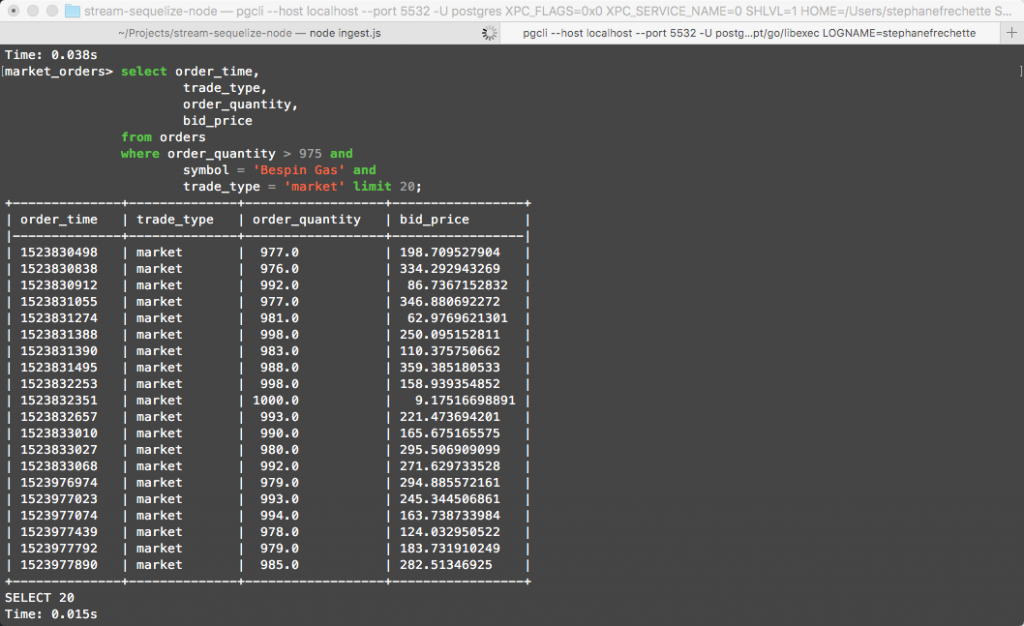
-- Orders with order quantity greater than 975...
select order_time,
trade_type,
order_quantity,
bid_price
from orders
where order_quantity > 975 and
symbol = 'Bespin Gas' and
trade_type = 'market' limit 20;
Enjoy!